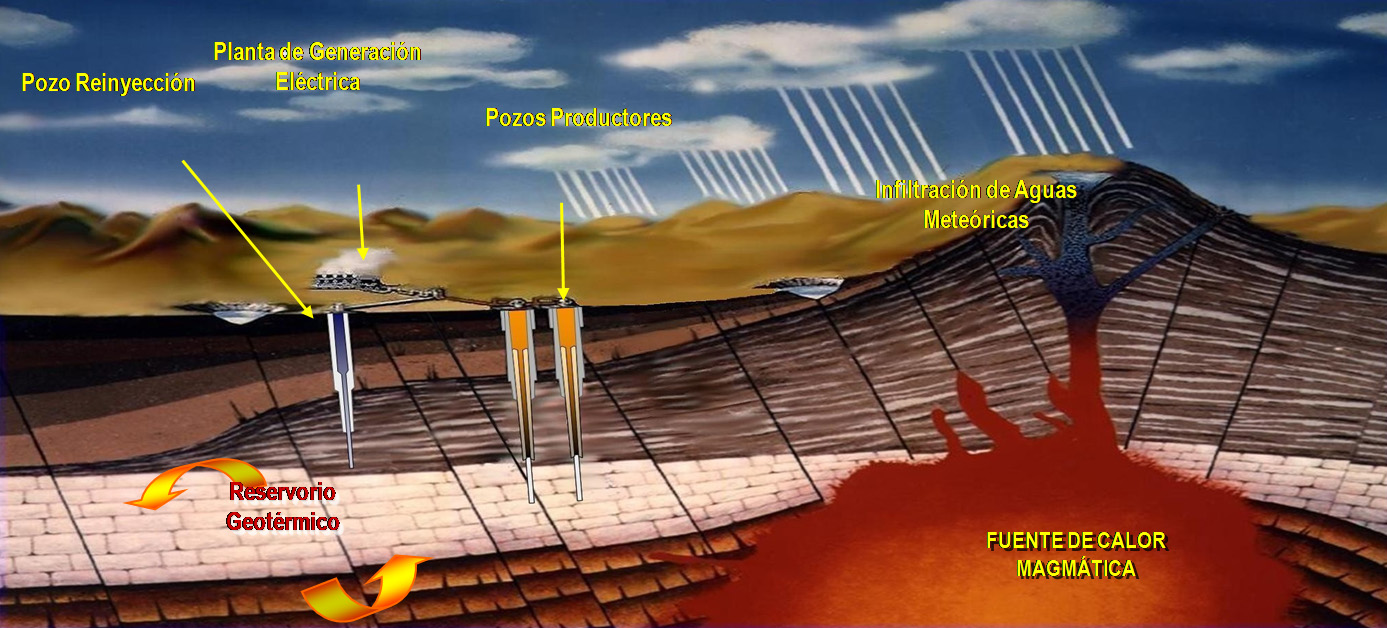
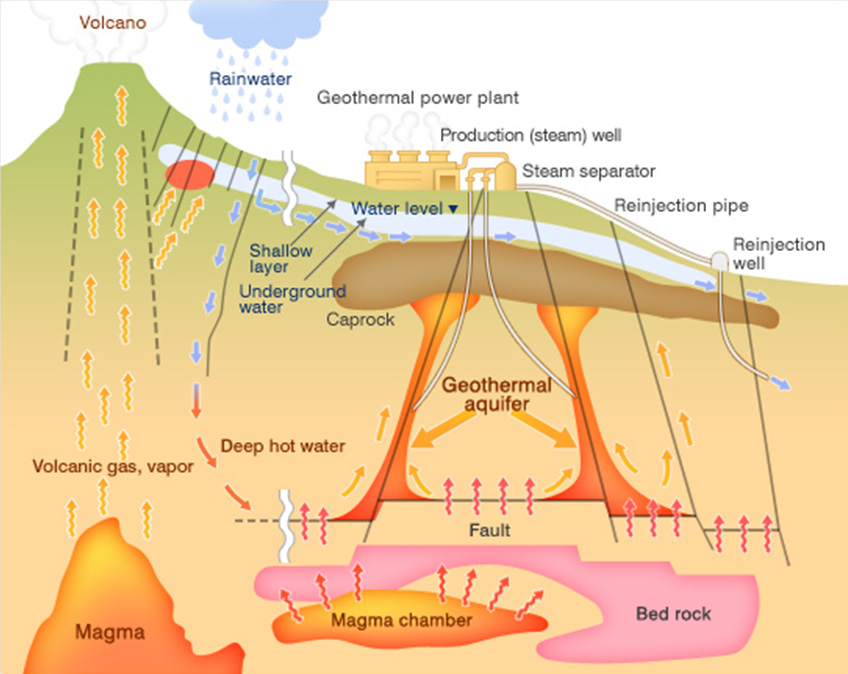
Geothermal energy is heat that comes from inside the earth. The word is the combination of the Greek words “geo” (earth) and “thermos” (heat).
For a geothermal resource to be industrially usable, it is necessary that a large amount of thermal energy be stored in permeable rocks and close to the surface (1-3 km).


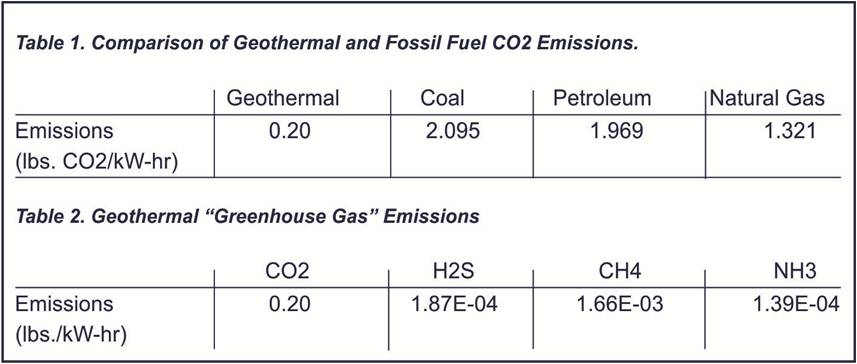
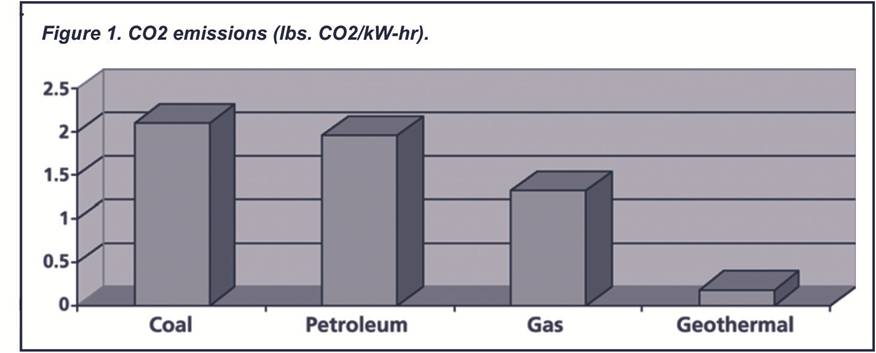
Due to geothermal plants not burning fossil fuels, they produce low levels of CO2 emissions. Geothermal production is currently estimated to prevent the emission of 22 million tons of CO2 per year, compared to coal-based electricity production. A case study of a coal plant including purifiers and other emission control technologies, emits 24 times more carbon dioxide (CO2), 10,837 times more sulfur dioxide (H2S) and 3,865 times more nitrogen oxides (NO3) per megawatt/hour than a geothermal steam plant.
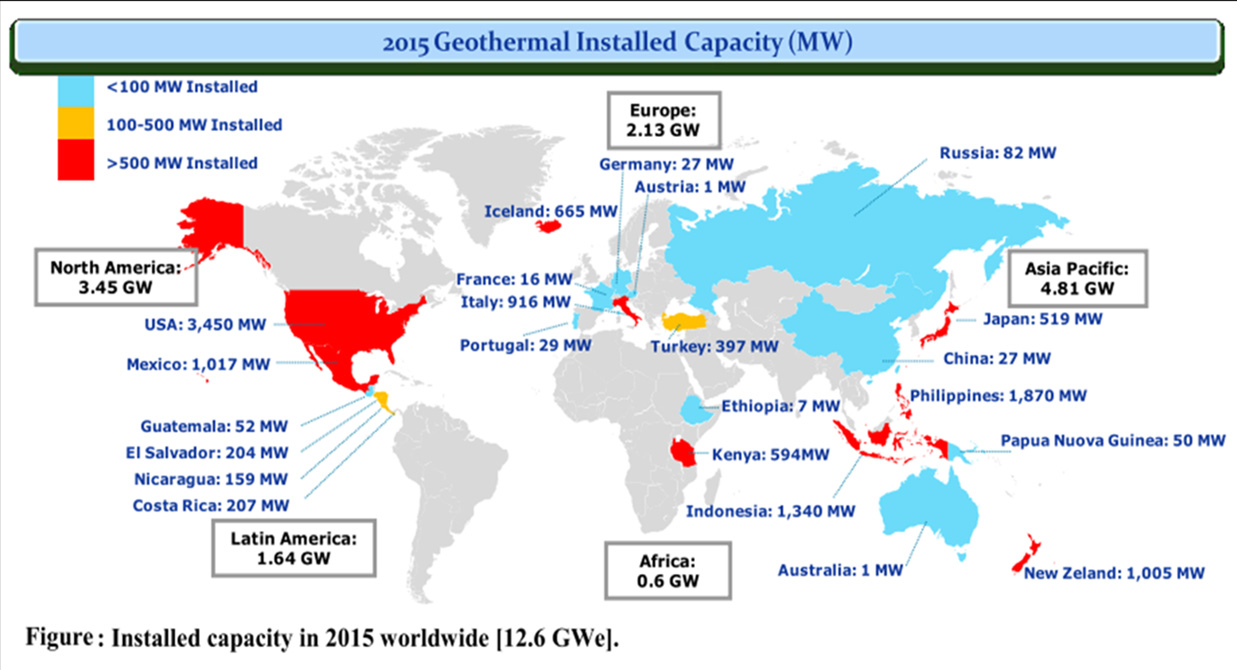
There are currently 24 countries that produce geothermal energy, reaching a total installed power of 12,600 MW * approx.
Note *: 10,800 MW of Flash Plants and 1,800 MW of Binary Plants
Power plant factors (percentages)

Chile’s geothermal potential would increase from 2,440 to 3,500 MW if other less explored projects are developed in the next 20 years.

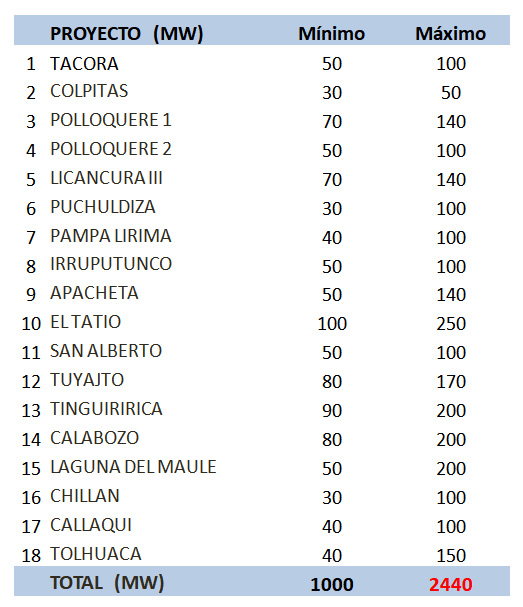

The energy needs of Chile and any other country must be envisaged using a horizon of several years and, in this context, geothermal energy is a viable option: